本次总结一下有关卡尔曼滤波器的用法及原理。
Kalman Filter
- Optimal estimation algorithm
- Common applications include guidance and navigation systems, computer vision systems and signal processing
- One of the very firt applications of the Kalman filter was the Apollo project
卡尔曼滤波器是一个最优的估计问题算法,那么就需要对于变量的值有个连续的估计,也就是说我们得到不是一个离散的值,而是连续值。
Kalman filter is used when:
卡尔曼滤波器经常被用在
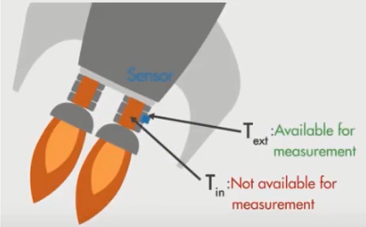
- The variables of interest can only be measured indirectly 即我们感兴趣的变量只能被间接得测量
例如火箭喷射器所喷射火焰的温度我们不能直接测量,但我们能够通过传感器测出火箭喷射器的温度然后估计出喷射火焰的温度。
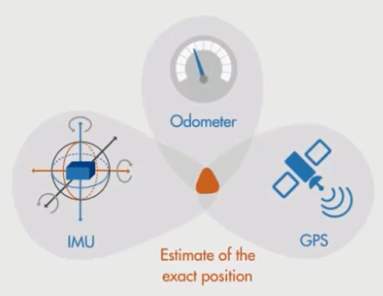
- Measurements are available from various sensors but might be subject to noise 还被用在有多种传感器的测量中,而且传感器的测量值存在噪声
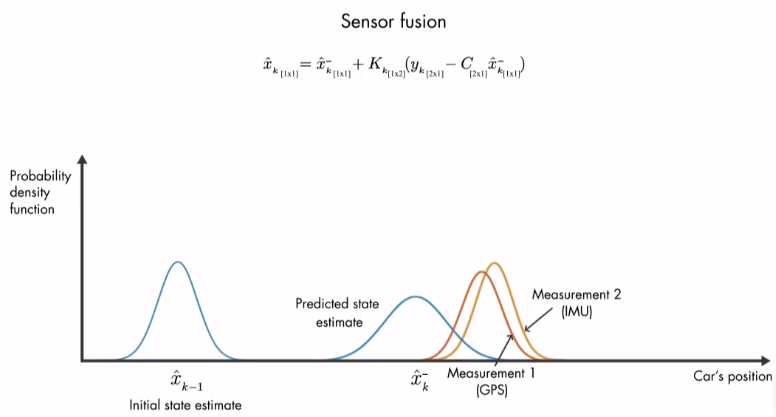
例如估计位置时需要用到 GPS 、 里程计 、 惯性测量单元(IMU) ,这些估计出的位姿存在一定的噪声,因此如何得到最优的估计,可以用卡尔曼滤波器解决。
卡尔曼滤波:利用线性系统状态方程,通过系统输入输出观测数据,对系统状态进行最优估计。
卡尔曼提出的递推最优估计理论,采用状态空间描述法,能处理多维和非平稳的随机过程。
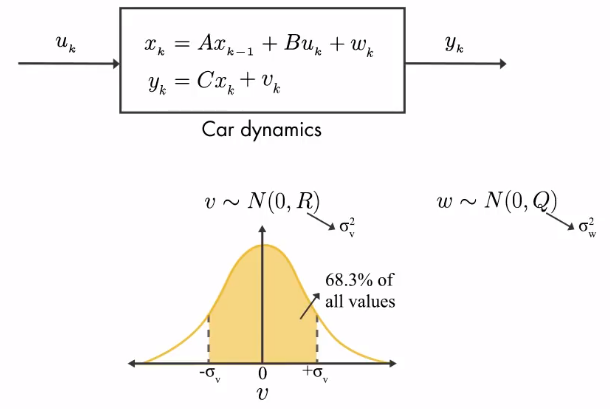
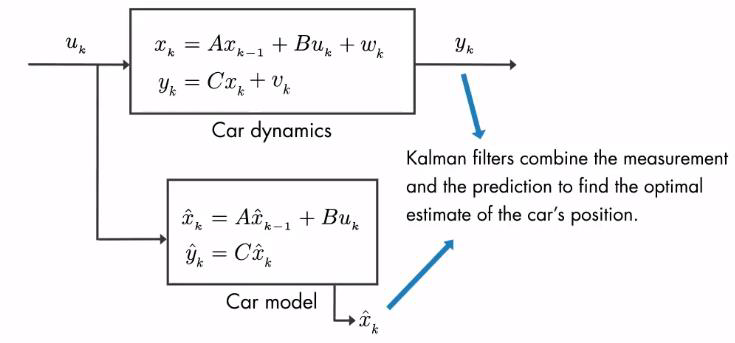
例如示图中:可以用线性状态空间表示车辆的 dynamics
我们使用 $u_k$ 表示对车辆的控制量例如踩油门,就是对车辆进行加速的控制(即输入), $y_k$ 是观测值,就是车辆的观测数据(即输出)。
$x_k$ 表示车辆状态否(位姿), $x_k$ 可以通过递推表示,意思是我们可以通过车辆之前的状态 $x_{k-1}$ 计算出当前状态。不过结果肯定是带有一定的噪声 $w_k$ 。其中 $A , B$ 指的是变换矩阵
$y_k$ 则是通过变换矩阵 $C$ 乘以 车辆状态 $x_k$ ,同样也会带有一定的噪声 $v_k$
其中噪声 $w_k$ 和 $v_k$ 都符合高斯分布,并且都有对应的均值方差
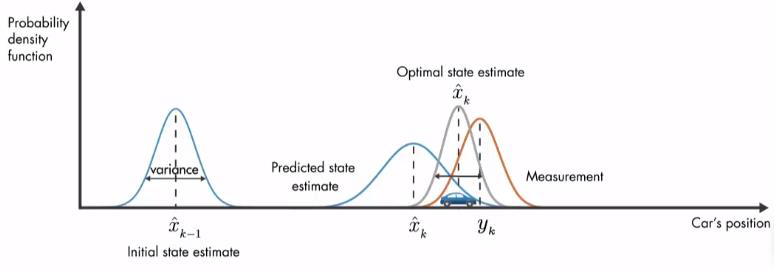
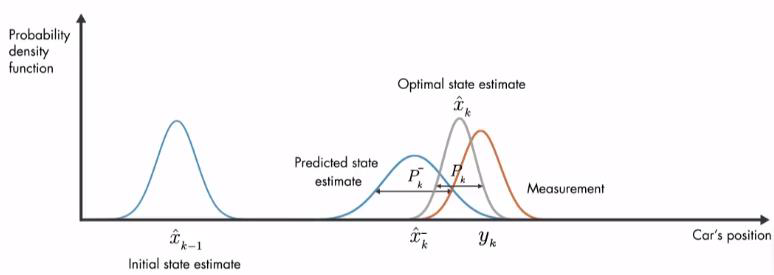
当然,我们还可以根据车辆模型来 car model 预测车辆的状态(位姿) $\hat{x}_k$ ,如图所示。卡尔曼滤波器能够根据当前的测量值 measurement 和预测值 prediction 进行加权求和来得到最优的车辆位姿估计。
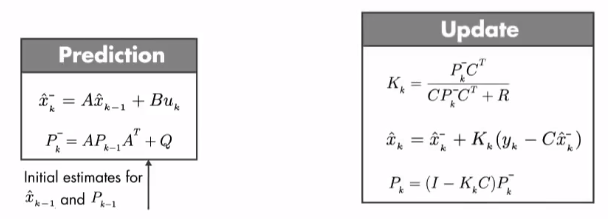
Kalman Filter 步骤
Kalman Filter 基本可以归纳为:“预测”(Predict)和“更新”(Update)两个步骤。
别忘了,我们假设所有的状态和噪声均满足高斯分布。记这里的噪声服从零均值高斯分布:
\[w_k \sim N(0, R) \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ v_k \sim N(0, Q)\]Prediction
\[\hat{x}^{\bar{}}_k = A\hat{x}_{k-1} + Bu_k\] \[P^{\bar{}}_k = AP_{k-1}A^T + Q\]预测过程中我们则是根据模型得到预测值(也称为先验) $\hat{x}^{\bar{}}_k$ 以及协方差 $P^{\bar{}}_k$
Update
\[K_k = \frac{P^{\bar{}}_kC^T}{CP^{\bar{}}_kC^T + R}\] \[\hat{x}_k = \hat{x}^{\bar{}}_k + K_k(y_k - C\hat{x}^{\bar{}}_k)\] \[P_k = (I - K_kC)P^{\bar{}}_k\]更新过程中,我们先计算 $K_k$ ,称为 卡尔曼增益 。然后计算后验 $\hat{x}_k$
完整过程如下:
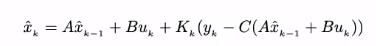
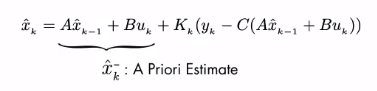
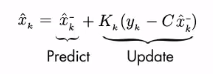
同样适用于多传感器融合
使用时一般忽略 $u$ 控制输入,得到:
| Time Update | Measurement Update |
|---|---|
| $\hat{x}^{\bar{}}k = A\hat{x}{k-1}$ | $K_k = P^{\bar{}}_kH^T(HP^{\bar{}}_kH^T + R)^{-1}$ |
| $P^{\bar{}}k = AP{k-1}A^T + Q$ | $\hat{x}_k = \hat{x}^{\bar{}}_k + K_k(z_k - H\hat{x}^{\bar{}}_k)$ |
| $P_k = (I - K_kH)P^{\bar{}}_k$ |
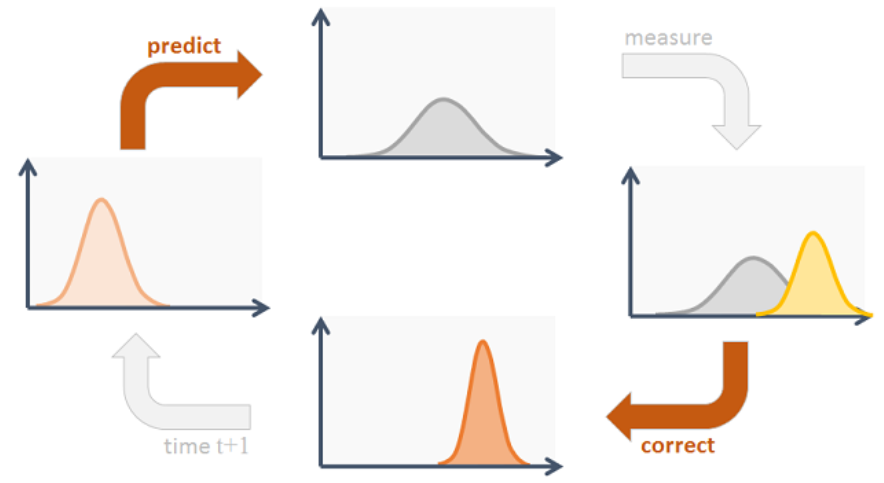
Cycle of a Kalman filter
即卡尔曼滤波器是如何处理连续多帧情况的。
Much of what the Kalman filter does can be reduced to propagating and updating Gaussians and updating their covariances. First the filter predicts the next state from the provided state transition (e.g. motion model), then if applicable, the noisy measurement information is incorporated in the correction phase. The cycle is repeated.