上一次,是讲解DeepSORT代码部分的各个模块,本次主要是梳理DeepSORT代码运行的流程。
本人使用的 Yolov5 + DeepSORT 的整体代码,所作出的分析也是基于此代码。代码地址在 https://github.com/mikel-brostrom/Yolov5_DeepSort_Pytorch 。
流程分析
流程部分主要按照以下流程图来走一遍:[图片来自博客]
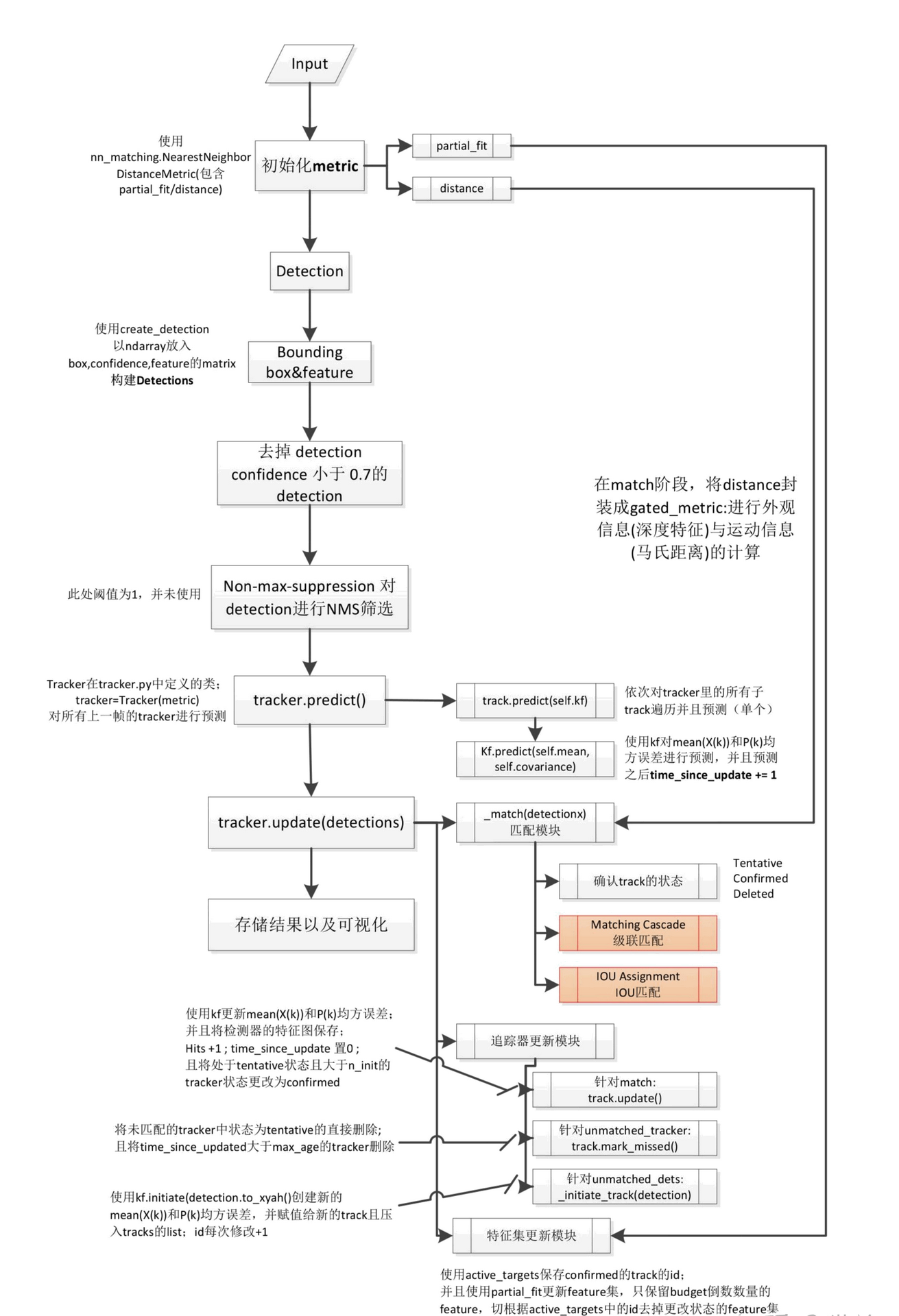
1. track.py
当 Yolov5 检测模型和跟踪模型都准备好以后,开始运行代码测试时,我们就从该运行代码 track.py 开始
1 | |
初始化DeepSORT对象,更新部分接收目标检测得到的框的位置,置信度和图片:
1 | |
2. 根据 deepsort 类的 update 函数看
1 | |
从这里开始对照以上流程图会更加清晰。在 deepsort 初始化的过程中有一个核心 metric , NearestNeighborDistanceMetric 类会在匹配和特征集更新的时候用到。
梳理 DeepSORT 的 update 流程:
- 根据传入的参数(bbox_xywh, conf, img)使用ReID模型提取对应bbox的表观特征。
- 构建 detections 的列表,列表中的内容就是
Detection类,在此处限制了bbox的最小置信度。 - 使用非极大抑制算法,由于默认nms_thres=1,实际上并没有用。
- Tracker 类进行一次预测,然后将 detections 传入,进行更新。
- 最后将 Tracker 中保存的轨迹中状态属于确认态的轨迹返回。
以上核心在 Tracker 的 predict 和 update 函数,接着梳理。
3. Tracker 的 predict 函数
Tracker 是一个多目标跟踪器,保存了很多个 track 轨迹,负责调用卡尔曼滤波来预测 track 的新状态+进行匹配工作+初始化第一帧。 Tracker 调用 update 或 predict 的时候,其中的每个 track 也会各自调用自己的 update 或 predict 。
1 | |
predict 主要是对轨迹列表中所有的轨迹使用卡尔曼滤波算法进行状态的预测。
Tracker 的 update 函数
Tracker的更新属于最核心的部分。
1 | |
这部分注释已经很详细了,主要是一些后处理代码,需要关注的是对匹配上的,未匹配的 Detection ,未匹配的 Trac k三者进行的处理以及最后进行特征集更新部分,可以对照流程图梳理。
Tracker 的 update 函数的核心函数是 match 函数,描述如何进行匹配的流程:
1 | |
对照如下图:
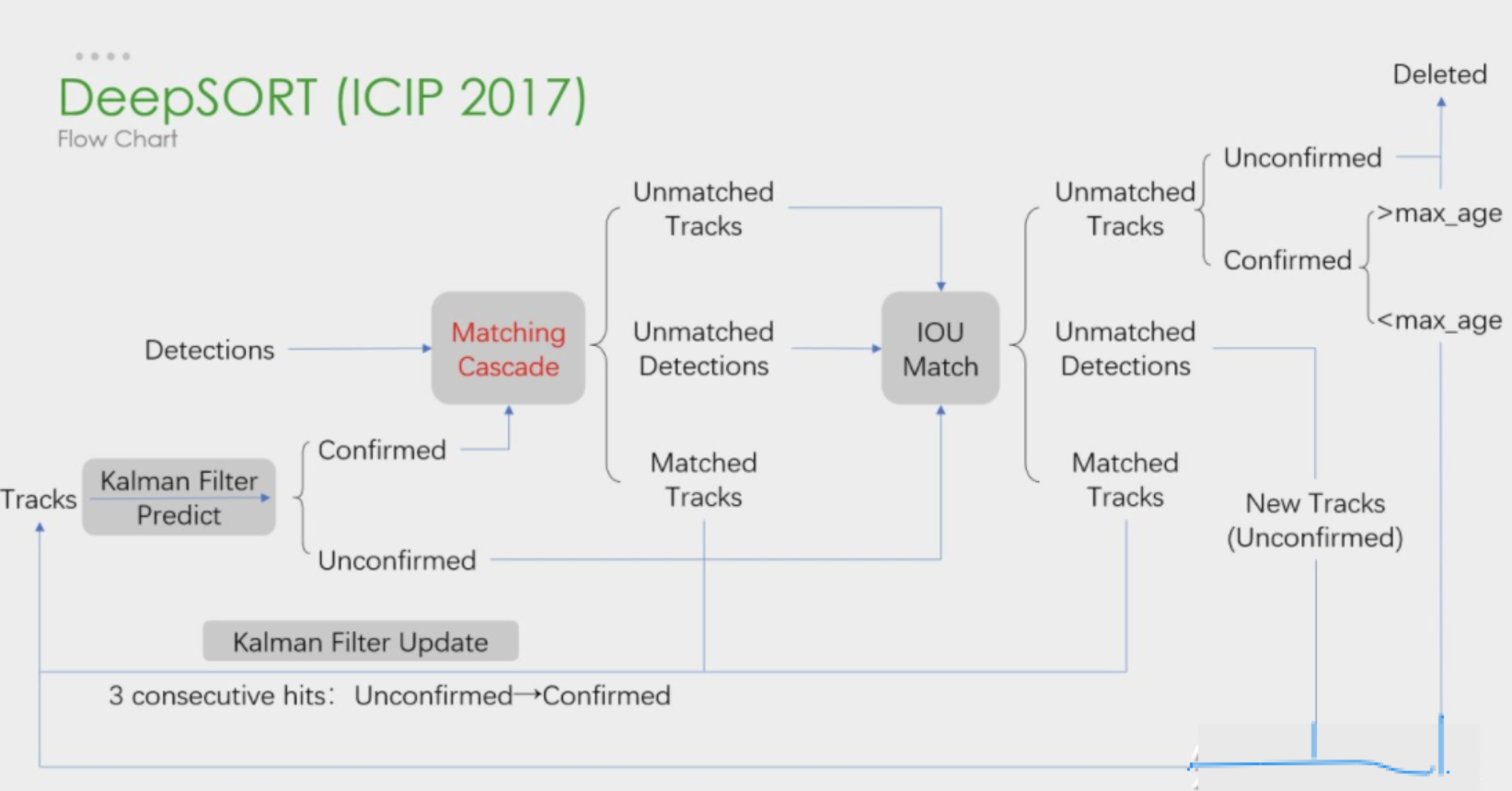
级联匹配函数
级联匹配函数展开:
1 | |
可以看到和伪代码是一致的,文章上半部分也有提到这部分代码。这部分代码中还有一个核心的函数 min_cost_matching ,这个函数可以接收不同的 distance_metric ,在级联匹配和IoU匹配中都有用到。
min_cost_matching 函数
1 | |
注释中提到distance_metric是有两个的:
- 第一个是级联匹配中传入的distance_metric是gated_metric, 其内部核心是计算的表观特征的级联匹配。
1 | |
- 第二个是IOU匹配中的iou_matching.iou_cost:
1 | |
iou_cost 代价很容易理解,用于计算 Track 和 Detection 之间的 IOU 距离矩阵。
1 | |
END